2021 – Global military spending 2,113 billion dollarsIncrease of 0.7 % from 2022 Increase of 12 % from 2012 1. USA ($801 billion, decrease of 1.4 % from 2020) 2. China ($293 billion, increase of 4.7 % from 2020 3. India ($76.6 billion, increase of 0.9 % from 2020) 4. Britain ($68.4 billion, increase of 3 % from 2020) 5. Russia |
|
| Ballistic missiles (21 launchers) | Yars
Avangard Sarmat |
| Submarines (3) | Borey-A |
| Missile Carriers | Tu-160M |
| Armoured and Artillery | More than 1000 pieces |
| Air Defence Systems (2) | S-400 Triumph |
| Short distance rocket systems | Gubka-S |
| Aircraft | Su-57 |
| Air Defence Systems (5) | S-400 Triumph |
| Missile Carriers (4) | Tu-95MS |
| Coastal Missile Systems (3) | Bastion |
| Anti-Aircraft Missiles and Cannon Systems | Pantsir-S
S-350 Vityaz |
| Aviation Equipment (151) | |
| Helicopters (29) | |
| Aircraft (77) | |
| UAV Complexes (45) | |
| Increase of 15% from previous year | |
| Conclusion of contracts: 85% (despite sanctions) | |
| Remuneration of military personnel | Indexed |
| Remuneration of civilian personnel | Indexed |
| Military pensioners, including combat veterans | Extended to relatives |
| Orders to state customers: 88% to 100% | |
| Participants of the military-industrial complex | |
| Rosatom | |
| Roscosmos | |
| Rostec | |
| JSC Concern of East Kazaghstan Region Almaz – Antey | |
| JSC USC | |
| JSC Tactical Missile Armament Corporation | |
| JSC Marine Instrumentation Corporation | |
| Creation of UAV complexes | Until 2027 and up to 2032 |
| Arctic | |
| 117 structures built (108%) | |
| 28 objects to be built in 2022 | |
| Military Districts | |
| 12 new units and sub-units in the Western district | |
| Training periods increased by 25% | |
| Training periods in the Baltic Fleet increased by 42% | More than 300 combat exercises |
Contracts awarded |
|
| Military Industrial Company LLC | BTR-82A armored personnel carriers |
| Tiger vehicles | |
| Armory Workshops LLC | Tiger-M car car with a remote-controlled combat module “Arbalet” |
| Uralvagonzavod | T-90M tanks |
| overhaul of the T-80BV | |
| 103rd Armored Repair Plant | overhaul of the BMP-2 with modernization |
| Design Bureau of Mechanical Engineering (KBM) | manufacture and supply of missiles for the Iskander-M complex |
| Tactical Missile Armament Corporation (KTRV) | supply of air-to-surface and air-to-radar aircraft missiles |
| Smolensk Aircraft Factory | manufacture and supply of air-to-ship aircraft missiles |
| Central Research Institute of Chemistry and Mechanics | UAB-20 guided aerial bombs |
| “Innovator-1” mobile complex for the destruction of toxic chemicals | |
| A.Ya. Bereznyak State Machine-Building Design Bureau Raduga JSC | long-range air-launched cruise missiles |
| Almaz-Antey concern of East Kazakhstan | S-500 air defense system |
| Aerospace Defense Concern Almaz-Antey | aviation and air defense control system |
| Total exceeting 522 billion rubles | More than 3,700 new models of equipment
Modernization of over 100 units of military and special equipment |
2022
Contracts signed at Army-2022 Forum |
36 state contracts |
| 525 billion rubles | |
| Portfolio: $592,650,000 and 1,770,000,000 rubles | |
Federal budget for 2023 |
|
| Increase by 302.9 billion rubles to 4,981.6 billion rubles | 2021: 3,573.6 billion rubles
2022: 4,678.7 billion rubles 2024: 4,648.8 billion rubles 2025: 4,206.1 billion rubles |
| 2 billion rubles for maintenance and equipment of Railway troops | Eastern polygon: 2.3 billion rubles |
| Reconstruction of the Ulak — Febralsk section of the Baikal-Amur mainline, length of 340 km | |
| 16 billion rubles for creation of the mobilization human reserve of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation | 15.96 billion rubles in 2023
16.53 billion rubles in 2024 16.53 billion rubles in 2025 |
| National defence: 13.7 trillion rubles for 2023-2025 | 2023: 4.9 trillion rubles
2024: 4.6 trillion rubles 2025: 4.2 trillion rubles |
| 2023: 3.3% of the GDP (increase by 17.1% from 2022)
2024: 2.9% of the GDP (decrease by 16.2% from 2022) 2025: 2.5% of the GDP (decrease by 15.1% from 2022) |
|
Development programme 2011-2020 |
|
| By 2015 modern weapons for army, navy and aviation – increase by 30% | |
| By 2020, increase by 70% | |
| Project 2007-2015 was not fully implemented | 4 trillion 939 billion 400 million rubles allocated
Armed Forces received 4 trillion 98 billion rubles or 83% |
Weapons Purchase Plans and their Realisation |
|||
| Weapons and Military Equipment | Project Implementation Unit 2007-2015 (Project) | Transfers to the AF of the RF 2007-2011 | Project Implementation 2011-2020 (Project) |
| Iskander Complex | 5 brigades | 1 brigade | 10 brigades |
| Aircraft | 116 | 22 | 600 |
| Helicopters | 156 | 60 | 1000 |
| Anti-Aircraft Systems | 18 divisions | 4 divisions | 56 divisions |
| Corvettes and Frigates | 12 | 2 | 50 |
| Nuclear-Powered attack submarines | 7 | 1 | 8 |
| Submarines | 6 | 0 | 20 |
| 400 modern land- and sea-based intercontinental ballistic missiles | |
| 8 strategic missile submarines | |
| About 20 multi-purpose submarines | |
| More than 50 combat surface ships | |
| About 100 military spacecraft | |
| More than 600 modern aircraft, including 5th generation fighters | |
| Over 1000 helicopters | |
| 28 regimental sets of S-400 anti-aircraft missile systems | |
| 38 divisional sets of Vityaz anti-aircraft missile systems | |
| 10 brigade sets of Iskander-M missile systems | |
| Over 2.3 thousand modern tanks | |
| About 2000 self-propelled artillery systems and guns | |
| More than 17,000 units of military vehicles | |
| Increase the number of formations and unis of permanent combat readiness to 600 | |
| 45% of the existing military equipment will be replaced |
Possible Combat Strength of the Russian Air Force for 2020 |
|||
| New | Modernised | Not Modernised | |
| Strategic and Long-Range Bombers | 0 | 16 Tu-160
36 Tu-95MS 30 Tu-22M3 |
20 Tu-95MS
70Tu-22M3 |
| Military Transport of Tankers | 39 Il-76MD-90A
30 Il-78MD-90A 60 An-70 50 MTA 30 L-410 20 An-148 10 An-140-100 100 Light Coastal Defence Systems 3 Tu-154M |
20 An-124-100
41 Il-76MDM |
4 An-124
60 Il-76MD 20 Il-78 5 An-22 No less than 20 An-26/30 No less than 10 Tu-154B No less than 10 Tu-134UBL |
| Special Purpose Aircraft | 2 Tu-204ON
2 Tu-204R No less than 5 A-100 |
No less than 10 Il-20
No less than 10 Il-22 12 A-50U |
|
| Tactical Aviation | 60 T-50
120 Su-35C 60 Su-30SM 4 Su-30M2 12 Su-27SM3 34 MiG-29SMT/UBM 140 Su-34 12 Su-25UBM 80 Ya-130 |
120 MiG-31BM
55 Su-27SM 120 Su024M/MR 10 MiG-25RB 150 Su-25SM |
150 Su-27
100 MiG-29 50 Su024M/MR 50 Su-25 100 L-39 |
| Army Aviation | 167 Mi-28N-NM
180 Ka-52 49 Mi-35M 38 Mi-26T/T2 500 Mi-8MTV/AMTSh 100 K-62 70 “Ansat-U” 36 Ka-226 100 light helicopters |
30 Mi-24PN
20 Mi-*MTKO 20 Mi-26T |
10 Ka-50
100 Mi-24V/P 300 Mi-8T/MTV 20 Mi-2 |
| Type of Troops | Proportion of Allocations, trillion rubles | Percentage | Planned to purchase or develop |
| Ground Troops | 2,6 | 15 | 2300 tanks, 2000 artillery systems, 10 brigade complexes of operational and tactical missiles Iskander-M, 9 brigade complexes of army air defence S-300V4, more than 30,000 units of automotive equipment |
| Military and Naval Fleet | 5,0 | 25 | 8 SSBN of Project 955, 8 multi-purpose submarines of Project 885, 12 non-nuclear submarines, 51 ships (including 15 frigates and up to 35 corvettes) |
| Air Force | 4,7 | 24 | 600 aircraft, 110 helicopters |
| Strategic Missile Forces | 1,0 | 5 | 270-280 ICBM Yars, development of new solid-fuel ICBMs Rubezh and new heavy liquid ICBM Sarmat |
| Aerospace Defence | 3,4 | 17 | 56 divisions of S-400, 38 division of S-500, 38 divisions of S-350, 120 Pantsir-S launchers, integrated management system of the aerospace defence, 4 Voronezh radar systems, 100 satellites |
| Other and Joint-Forces | 2,7 | 14 | New communication, management and intelligence systems |
| Total | 19,4 | 100 |
Tanks and Infantry Fighting Vehicles |
|
| Upgraded T-72B3 tanks | |
| T-90M | |
| New generation of Armata tank T14 | |
| Modern BMP-3 | |
| Upgraded BMP-2 | Installation of the Bereshok combat compartment installed |
| B-11 Kurganets-25 being tested | |
| BTR-82AM | |
| BTR-K17 Boomerang being developed |

Russian warships are seen during a rehearsal for the Navy Day parade in Sevastopol, Crimea, July 24, 2015. REUTERS/Pavel Rebrov
Construction of Ships for the Russian Navy as part of the Russian State Armament Development Program for 2011-2020 |
|
| 10 cruiser submarines – Project 955/955A/955U | |
| 10 nuclear all-purpose submarines – Project 855/855M | |
| 6 submarines – Project 636.3 Varshavianka | |
| 14 submarines – Project 577 Lada | |
| 4 helicopter carriers Mistral | |
| 35 corvettes | |
| 10 small rocket ships – Project 31631 | |
| 6 frigates – Project 11356 | |
| 6 large landing ships – Project 11711 | |
| 8 frigates – Projects 22350 | |
| DECREE OF THE PRESIDENT OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION NO. 603 OF MAY 7, 2012 | |
| CONSTRUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT OF THE ARMED FORCES OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION, OTHER TROOPS, MILITARY FORMATIONS AND BODIES AND THE MODERNIZATION OF THE MILITARY-INDUSTRIAL COMPLEX | |
| a) equipping the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation, other troops, military formations and bodies with modern models of weapons, military and special equipment, bringing their share to 70 percent by 2020 | |
| b) priority development of nuclear deterrence forces, means of aerospace defense, communication, intelligence and control systems, electronic warfare, unmanned aerial vehicle complexes, robotic strike complexes, modern transport aviation, precision weapons and means of combating them, systems of individual protection of military personnel | |
| c) development of the Navy, primarily in the Arctic zone of the Russian Federation and in the Far East, in order to protect the strategic interests of the Russian Federation | |
| d) implementation in 2012 of the following activities | creation of a qualitatively new system of analysis and strategic planning in the field of countering threats to national security for a period of 30 to 50 years in the interests of the formation of state armament programs |
| expanding the practice of holding open tenders and auctions within the framework of the implementation of the state defense order and increasing responsibility for violating the requirements established by legislative and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation in the field of the state defense order | |
| improvement of the regulatory framework in the field of state defense orders and pricing for military products | |
| simplification of the procedure for creating new production facilities for military products, including through the implementation of the mechanism of public-private partnership | |
| creation of a management system for the full industrial cycle of production of weapons, military and special equipment — from modeling and design to serial production of products, ensuring their operation and further disposal | |
| creation of a system aimed at improving the management of the economic activities of defense industry organizations in order to optimize production processes that allow the use of advanced technologies, including foreign ones, to create high-quality products | |
| ensuring the dynamic development of breakthrough high-risk research and development, fundamental science and the implementation of applied research programs in the interests of national defense and state security, including with the participation of the Russian Academy of Sciences, state research centers and leading universities | |
| preparation of methodological recommendations on the formation of the draft state armament program for 2016-2025, which provides for the comprehensive rearmament of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation, other troops, military formations and bodies on the basis of competitive domestic models of weapons, military and special equipment | |
| e) preparation of proposals in 2012 | on the creation of federal executive bodies subordinate to the Government of the Russian Federation, performing the functions of placing a state defense order and monitoring its execution |
| to clarify the Rules for the development and implementation of state weapons programs | |
| to create a unified information base of research and development works, the results of intellectual activity and technologies of military, special and dual-use, design documentation for military products for their use in the creation of innovative dual-use and civilian products | |
| to improve the system of vocational education of employees of organizations of the military-industrial complex, to improve the standard of living of these workers, as well as to build residential premises for them | |
| PRIORITY TASKS | |
| Continue building up the combat capabilities of the Armed Forces | |
| Take measures to strengthen the groupings of troops in the Western, South-Western and Arctic strategic directions | |
| To ensure timely deployment and strict execution of the tasks of the GOZ-2017 and to reach the equipping of the Armed Forces with modern weapons and equipment in units of constant readiness of more than 60% | |
| Strategic Nuclear Forces (para.149) | |
| Strategic Missile Forces | 1 Tu-160
4 Tu-95MS |
| General Purpose Forces | |
| 2 brigade sets of Iskander-M missiles for ground forces | |
| Re-equip 3 division of air defence with Tor-M2 anti-aircraft systems | |
| Supply 905 modern tanks and armoured combat vehicles | |
| Accept 170 new and upgraded aircraft by the Aerospace Forces and Navy | |
| Re-equip 4 anti-aircraft missile regiments with S-400 anti-aircraft missile systems | |
| Introduce 8 surface ships to the Navy | |
| Introduce 9 combat boats to the Navy | |
| Commissioning and putting on combat duty 3 radar stations in Yeniseisk, Orsk and Barnaul | |
| Launch the second spacecraft of the United Space System |

Russian Defence Minister Sergei Shoigu salutes during the 72nd anniversary of the end of World War II on the Red Square in Moscow, on May 9, PHOTO: REUTERS
| EXECUTION OF THE STATE DEFENSE ORDER IN 2018 (para. 161) | |
| Funds allocated (2018): 1.5 trillion rubles | |
| About 70 per cent of these funds allocated to series procurement | |
| Provided solutions to problematic issues of placement and execution of tasks of the State Budget with integrated structures and directly with organizations of the defense industry complex (MIC) – executors of state contracts | |
| Rearmament of the Russian Strategic Nuclear Forces group will be done taking into account the implementation of the US concept of “Global Strike” and the deployment of global missile defense | |
| Measures taken made it possible to contract the main amount of funds in a timely manner, by May 15, which is about 94 percent, and to begin implementing the tasks of the State Budget | |
| About 115,000 units of modern models and equipment have been delivered to the troops, including more than 2,500 basic air force units that determine the combat power of the types and types of troops: | Su-30SM and Su-35S fighters, Su-34 front-line bombers, Yak-130 combat training aircraft, Ka-52, Ka-226, Mi-8 helicopters of various modifications. In total – more than 120 units of aviation equipment |
| large deliveries of new BMP-3, BTR-82A armored personnel carriers, as well as amphibious BTR-MDM and BMD-4M. In total – more than 300 units of armored weapons and equipment | |
| Rocket and artillery armament for the current year, ATGMs “Chrysanthemum-SP” and “Kornet”, self-propelled howitzers “Msta-SM”, a divisional set of ATGMS “Iskander-M”, cruise missiles “Caliber” and “Onyx” were delivered to the troops. In total – more than 120 units of rocket and artillery weapons | |
| Frigate of project 22350 “Admiral of the Fleet of the Soviet Union Gorshkov”, the MRK of project 22800 “Mytishchi” and project 21631 “Orekhovo-Zuyevo” were accepted into the structure. Various combat boats and support vessels, as well as coastal missile systems “Bal” and “Bastion” were received. On December 25, the corvette 20380 “Loud” will be transferred to the TOPF. In total – more than 20 ships and vessels of various purposes | |
| In 2018, the Armed Forces were replenished with the Pantsir-S air defense system, the Tor-M2 air defense system, including the Arctic version, the Buk-M3 air defense system, the S-400 Triumph air defense system | |
| Troops received over 100 complexes of radar stations for various purposes, small arms and equipment, communications equipment, RCBZ, the latest electronic warfare systems and much more | |
| About 8,500 repaired and modernized models and weapons, including more than 2,000 basic ones, have been returned to service. More than 57,000 armaments and military and special purpose equipment units were serviced directly for the troops | |
| the level of equipment of permanent readiness units with modern serial models of the Air Force to 61.5 percent, and the provision of troops with weapons and equipment to 98 percent and to maintain the serviceability of the fleet at about 94 percent | |
| In accordance with the May 2012 presidential decrees of the Russian Federation, the Ministry of Defense has developed and implemented an Activity Plan until 2020 | In six years, the Armed Forces received 109 intercontinental ballistic missiles “Yars”; 108 ballistic missiles submarines; three strategic missile submarines “Borey”; 57 spacecraft; seven submarines; 17 coastal missile systems “Bal” and “Bastion”, as well as 3712 new and upgraded tanks and other armored combat vehicles; more than 1,000 aircraft and helicopters; 161 surface ships, boats and vessels |
| 12 missile regiments for the Yars complexes were re-equipped; 10 missile brigades for the Iskander complex; 13 aviation regiments for the MiG-31BM, Su-35S, Su-30SM, Su-34; three army aviation brigades and six helicopter regiments for the Ka-52 and Mi-28; 20 anti-aircraft missile regiments for the S-400 anti-aircraft missile system; 23 divisions for the Pantsir-S complex; 17 divisions for the Bal and Bastion missile systems | |
| The number of failures of new weapons and equipment has been reduced by 2.7 | |
| The measures taken made it possible to increase by 2019 the number of carriers of high–precision long-range land, sea and air-based weapons by more than 12 times, and high-precision cruise missiles by more than 30 times | |
| By 2019, a continuous radar field of the missile attack warning system has been created along the perimeter of the Russian border in all strategic aerospace directions and along all types of ballistic missile flight paths | |
| A unified space detection and combat control system is being deployed | |
| A new space rocket complex “Angara” has been created | |
| Almost all Ground forces, as well as motorized rifle brigades and naval infantry brigades – a total of 35 formations – are provided with modern combat equipment “Ratnik-2” | |
| By 2019, the equipment of the Armed Forces with modern weapons increased 3.8 times – from 16% to 61.5% | |
| In the Strategic Nuclear Forces, it is 82%, in the Ground Forces – 48.3%, the Aerospace Forces – 74%, the Navy – 62.3%, the Airborne Forces – 63.7% | |
| New type of Armed Forces: | the Aerospace Forces |
| the formation of the USC “Northern Fleet” | |
| three armies: combined arms, tank, air Force and air defense army | |
| four army corps | |
| 25 formations | |
| more than 150 military units and organizations | |
| Crimea has been strengthened, which ensures the protection of the peninsula’s territory and Russia’s interests in the Black Sea | |
| An Operational Command has been established in the Far Sea zone, which provides control of ships performing tasks in the Mediterranean Sea | |
| In six years, 38 military units have been formed, which have been armed with more than two thousand modern drones | |
| In total, 316 samples of modern weapons in Syria were tested | |
| By 2019, a continuous radar field of the missile attack warning system has been created along the perimeter of the Russian border | |
| the number of annual combat training events has increased six and a half times compared to 2012 – up to 18 thousand. The number of annual interspecific exercises has increased 2.7 times – up to 1,500, and bilateral exercises 57 times – up to about 1,700 | |
| Since December 1, 2014, the National Defense Control Center of the Russian Federation has been on combat duty | |
| A system of centers and control points of the Armed Forces has been created | |
| A network of secure video conferencing has been deployed, numbering over 210 fixed terminals and 70 mobile sets | |
| New digital telecommunications equipment has been installed at more than 1,200 facilities of the Ministry of Defense – in almost every unit and military unit, in all military educational institutions | |
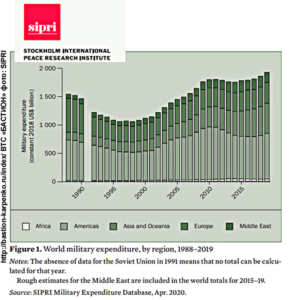
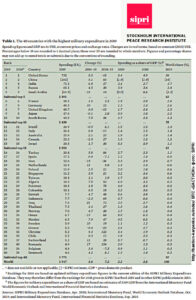
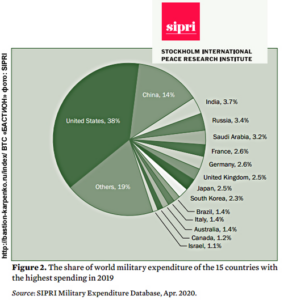
The Stockholm International Peace Research Institute SIPRI new report “Trends in world military expenditure, 2019” |
|
| Global military spending in 2019 is estimated at $ 1917 billion | highest level since 1988 |
| 3.6 percent higher than in 2018 | |
| 7.2% higher than in 2010 | |
| Growth is primarily due to an increase in US military spending | increased by 5.3 percent and reached $ 732 billion |
| Top five countries with the largest military expenditures also included China, India, Russia and Saudi Arabia | China’s military spending last year increased by 5.1 percent and reached $ 261 billion |
| India increased its military spending by 6.8 percent to $ 71.1 billion | |
| Russian Federation ranked fourth in the world in terms of military spending in 2019 with an indicator of $65.1 billion or 3.9% of GDP | Between 2018 and 2019, Russia’s military spending increased by 4.5 percent, and its military burden increased from 3.7% of GDP to 3.9%. |
| The defense budget in 2018 amounted to $61.4 billion (2.8% of GDP) | |
| Largest increase in spending among the 15 countries with the largest military expenditures in the world in 2019 fell on Germany | 10% (49.3 billion dollars) |
| The countries in the top five — the United States, China, India, Russia and Saudi Arabia — account for 62% of total military spending in the world, according to the SIPRI report | |
The Armed Forces of the Russian Federation. Development from 2012 to 2020 |
|
| The share of modern designs in strategic nuclear forces (SNF) has increased: | from 42% to 81% of ground-based strategic nuclear forces |
| from 46% to 89% in marine strategic nuclear forces | |
| from 22% to 88% in aviation strategic nuclear forces | |
| from 37% to 86% armaments and military and special purpose equipment in the SNF | |
| the number of carriers of long-range cruise missiles in strategic non-nuclear forces has increased 13 times | |
| the number of long-range cruise missiles in strategic non-nuclear forces has increased 37 times | |
| The share of modern armaments and military and special purpose equipment samples by species and generation has increased: | from 16% to 70.1% of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation |
| from 15% to 55.4% in the Ground Forces | |
| from 30% to 85.9% in the Aerospace Forces | |
| from 52% to 65.7% in the Navy | |
| from 42% to 81% in the SMF | |
| from 18% to 71.6% in the Airborne | |
The main results of the activities of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation in 2012-2020 |
| The Armed Forces of the Russian Federation conducted 10 successful launches of the Yars strategic complex in the period from 2012 to 2020 |
| In 2012-2020, five successful launches of an intercontinental ballistic missile with hypersonic gliding Avangard cruise blocks were also carried out |
| The number of complexes “Yars” and “Avangard” increased in 2012-2020 by 14 times and four times, respectively |
| The number of carriers of long-range cruise missiles in the Russian army increased 13 times in the period from 2012 to 2020 |
| The number of long-range land, air and sea cruise missiles increased 37 times in 2012-2020 |
| The refinement of strategic aviation aircraft for the use of new cruise missiles led to an increase in their combat capabilities by 1.7 times |
| More than 900 unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) have been delivered to the Russian army since 2012 |
| A total of 551 units of basic samples of rocket and artillery weapons (RAV) were delivered. The share of modern RAV models has been increased by more than 70%, including 22 anti-aircraft missile systems, 270 artillery units and multiple launch rocket systems, 188 anti-tank missile systems and 71 reconnaissance vehicles |
| The share of modern armaments and military and special purpose equipment has increased 70 times |